New Asteroid Threat Could Wipeout Mankind Like Dinosaurs?
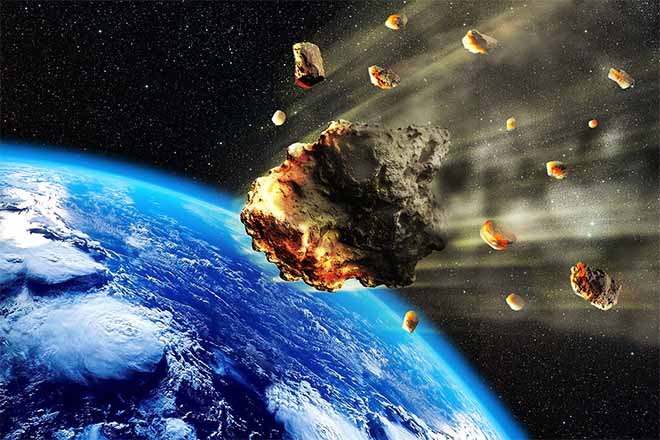

65 million years ago, the Earth experienced one of the biggest biological disasters in its history: in the oceans, half of the species of invertebrates and almost 90% of plankton disappeared. On dry land, half of the vertebrates, including the famous dinosaurs, are eliminated.
This massacre is believed to be due to the collision of a large asteroid about 10 km in diameter, which fell in the Chicxulub region (Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico), while the region was covered by the waters of the 'Atlantic. The crater (160 km in diameter!), currently buried under 1,000 m of sediment, was identified a few years ago. Under the violence of the impact, a gigantic tidal wave - the height of the wave is estimated at 500 m! - swept the American and Mexican coasts, while more than 50,000 km3 of dust and aerosols were projected into the atmosphere, plunging the Earth into cold and darkness.
The disappearance of the dinosaurs
With the slowing down, even stopping, of photosynthesis, the death of many plant species would have led to that of the herbivores and then logically that of the carnivores. The “stars” of the time, the dinosaurs, most often too large, too fragile, and unable to adapt to new difficult climatic conditions, disappear irreparably.
But is this asteroid impact the primary cause of extinction, or is it a kind of “knockout” given to ecosystems already weakened by the consequences of the receding oceans and the increase in continental surfaces, during the second half of the Cretaceous, and then by those of the gigantic volcanic eruptions which occurred in western India at the end of Secondary and at the very beginning of Tertiary? In fact, we would have to know whether the disappearance of the species was sudden or not.
New asteroid threat
Nevertheless, both in cinematographic fictions and following astronomical observations, we are seriously considering a “scenario” which would see the Earth devastated by a new asteroid impact. Meteorites are constantly falling on Earth's surface, most often without doing too much damage. And larger asteroids also pass regularly near our planet. “Nearby” means, for astronomers, at least a few hundred thousand kilometers away, in other words a distance comparable to that of Earth-Moon. This is both very little, given the cosmic distances, and sufficient to avoid the Earth from suffering another major cataclysm, even if the probability of such a collision is negligible.