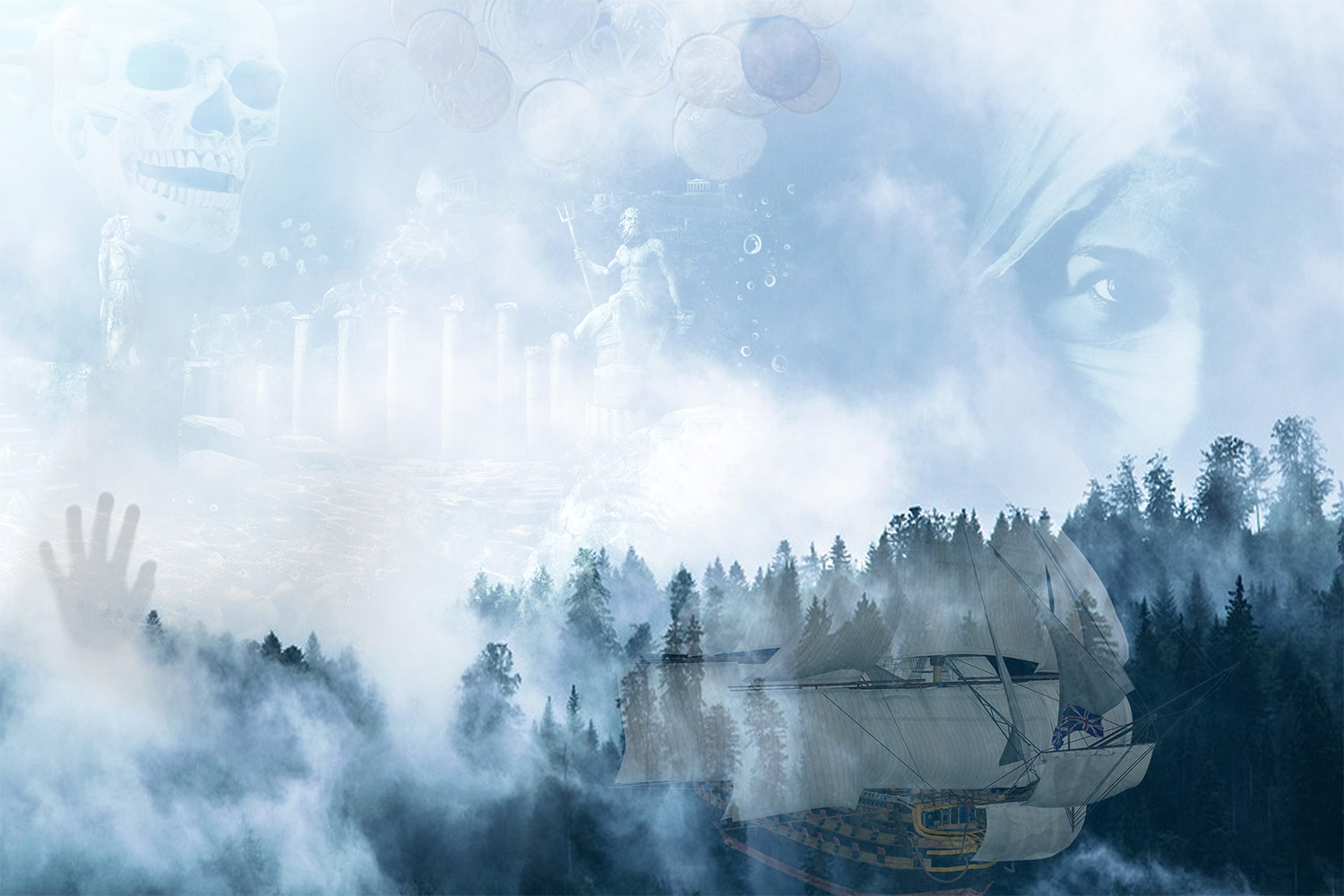
The Antikythera Mechanism
An Ancient Stellar Computer ?

In 1900, the wreck of a ship sunk in 80 BC was found off the island of Antikythera, between Crete and the Greek coast. Inside, archaeologists discover an object that resembles a block of worthless rusty metal: they are still unaware that they have in their hands what will be at the heart of one of the great mysteries of history. The objects will be brought back to the National Archaeological Museum of Athens where they are kept today. Months later, by analyzing the block in question, the archaeologist Valerios Strais discovers its true nature: it is a complex mechanism which has no less than thirty gears engraved with Greek inscriptions. Despite the incrustations due to the very long immersion in water, we can still see the cogwheels perfectly modeled in bronze. This shows a constructive and conceptual mastery that the Greeks, to our knowledge, did not have. So what exactly is it and where does this object that is now known as the Antikythera mechanism or Antikythera machine come from ?
An ancient stellar computer
The American University of Yale devotes in-depth studies to it. Thanks to the patient work of Professor Derek John de Solla Price, an English physicist, the Antikythera mechanism ends up being reconstructed and revealing some of its secrets. It is an astronomical calculator, a kind of ancient computer capable of predicting the relative positions of the stars, the Moon, the Sun and the Earth over time. At the time, the Antikythera machine must have looked very different from what it presents today. In fact, it is believed that it must have been inside a protective shell which made it possible to adjust the gears from the outside, by sorts of knobs. It would therefore be a technologically sophisticated object testifying to ancient knowledge which we ignore even its existence. Today's archaeologists agree that the Greeks and other peoples of Antiquity did not master such advanced technology. Some of the parts of the Antikythera mechanism - a kind of differential gear - are so innovative that their invention only dates back to the 16th century. One can also wonder why no other copies of this gear mechanism has been found ?
Timeless objects
Most often, they are called OOPART, acronym for Out of Place Artifacts. We prefer to just call them “timeless objects”, because they should not exist, or at least not at the time from which they seem to date. Indeed, the real difficulty consists in the fact of arriving at a dating which is coherent compared to what we know of human evolution. Therefore, in the face of certain archaeological objects such as the Antikythera mechanism, Carbon 14 and the electron microscope are not enough, and other instruments should probably be invented. By admitting that they are indeed authentic and not faked objects ...
We have been debating for years the origin and use of objects like that of the Antikythera mechanism, as well as inscriptions in unknown languages and apparently anachronistic drawings. In Africa, for example, clay statuettes have been found, Nomoli figurine, which seem to be around 17,000 years old. A chrome and steel ball is inside one of them, which could in no case exist at the time. What if we had to rewrite certain pages of our history ?
The hammer in the rock

It is called the London Hammer after the small town in Texas near which it was found in 1936. It is said that it was naturally embedded in stone and therefore in a relatively easy dating context. It looks like a contemporary hammer in every way. It goes without saying that there are many doubts about its authenticity, because if that were the case it would be necessary to review the whole of the theory of human evolution. It is not known if Carbon 14 analyzes have been done; in all cases, the wooden handle does not seem fossilized.